- java.lang.Object
-
- reactor.core.publisher.Flux<OUT>
-
- reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor<T,T>
-
- reactor.core.publisher.UnicastProcessor<T>
-
- 类型参数:
T- the input and output type
- 所有已实现的接口:
- java.lang.Iterable<T>, java.util.Collection<T>, java.util.Queue<T>, org.reactivestreams.Processor<T,T>, org.reactivestreams.Publisher<T>, org.reactivestreams.Subscriber<T>, org.reactivestreams.Subscription, CorePublisher<T>, CoreSubscriber<T>, Disposable, Fuseable, Fuseable.QueueSubscription<T>, Scannable
已过时。to be removed in 3.5, prefer clear cut usage ofSinksthrough variations underSinks.many().unicast().
@Deprecated public final class UnicastProcessor<T> extends FluxProcessor<T,T> implements Fuseable.QueueSubscription<T>, Fuseable
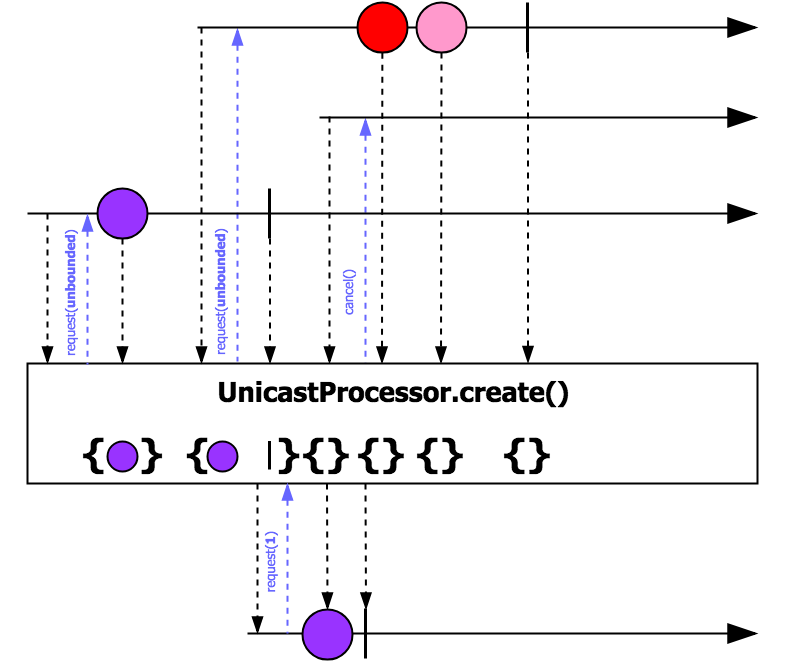
A Processor implementation that takes a custom queue and allows only a single subscriber. UnicastProcessor allows multiplexing of the events which means that it supports multiple producers and only one consumer. However, it should be noticed that multi-producer case is only valid if appropriate Queue is provided. Otherwise, it could break Reactive Streams Spec if Publishers publish on different threads.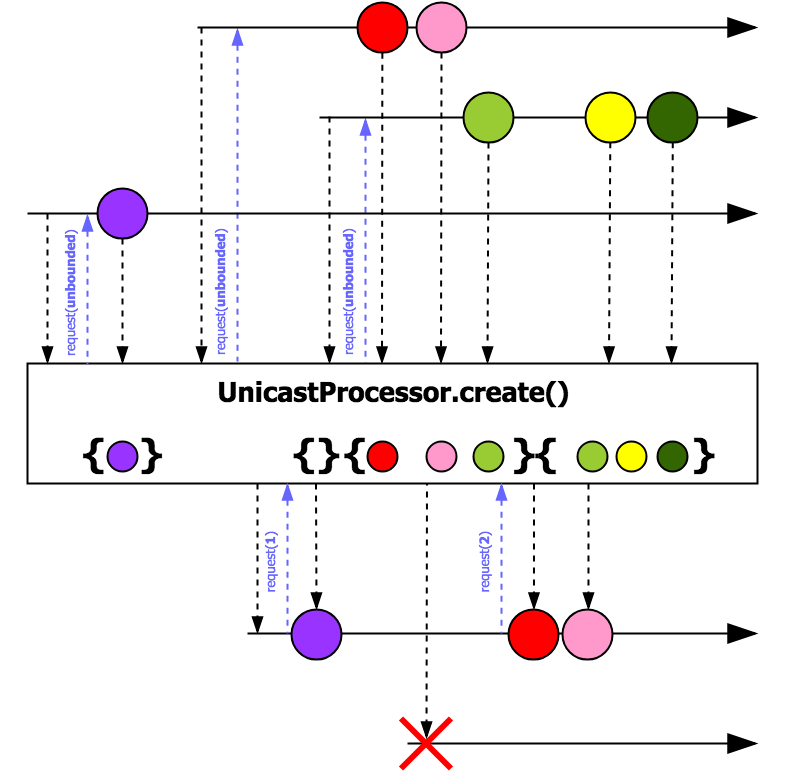
Note: UnicastProcessor does not respect the actual subscriber's demand as it is described in Reactive Streams Spec. However, UnicastProcessor embraces configurable Queue internally which allows enabling backpressure support and preventing of consumer's overwhelming. Hence, interaction model between producers and UnicastProcessor will be PUSH only. In opposite, interaction model between UnicastProcessor and consumer will be PUSH-PULL as defined in Reactive Streams Spec. In the case when upstream's signals overflow the bound of internal Queue, UnicastProcessor will fail with signaling onError( reactor.core.Exceptions.OverflowException).
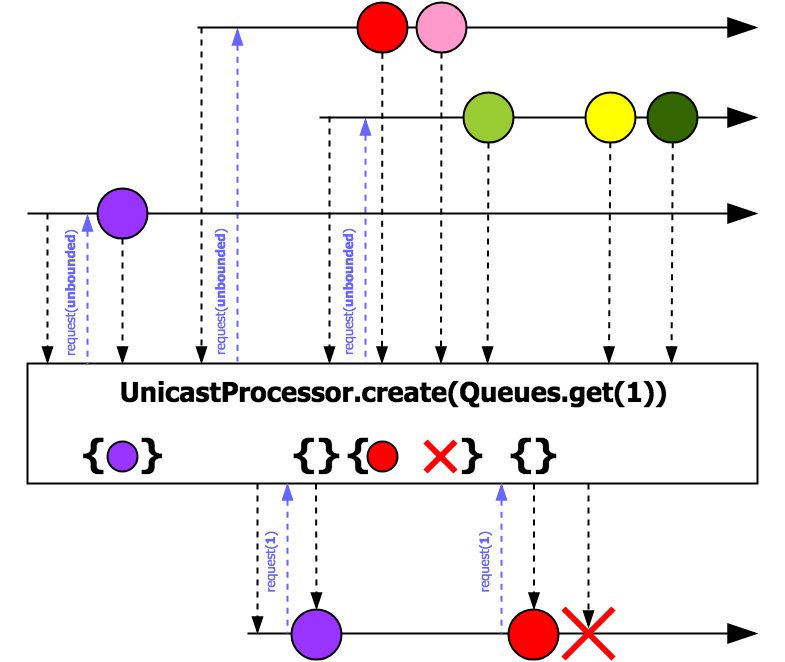
Note: The implementation keeps the order of signals. That means that in case of terminal signal (completion or error signals) it will be postponed until all of the previous signals has been consumed.
-
-
嵌套类概要
-
从接口继承的嵌套类/接口 reactor.core.Fuseable
Fuseable.ConditionalSubscriber<T>, Fuseable.QueueSubscription<T>, Fuseable.ScalarCallable<T>, Fuseable.SynchronousSubscription<T>
-
从接口继承的嵌套类/接口 reactor.core.Scannable
Scannable.Attr<T>
-
从接口继承的嵌套类/接口 reactor.core.Disposable
Disposable.Composite, Disposable.Swap
-
-
字段概要
-
从接口继承的字段 reactor.core.Fuseable.QueueSubscription
NOT_SUPPORTED_MESSAGE
-
从接口继承的字段 reactor.core.Scannable
OPERATOR_NAME_UNRELATED_WORDS_PATTERN
-
-
构造器概要
构造器 构造器和说明 UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue)已过时。UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue, java.util.function.Consumer<? super T> onOverflow, Disposable onTerminate)已过时。UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue, Disposable onTerminate)已过时。
-
方法概要
所有方法 静态方法 实例方法 具体方法 默认方法 已过时的方法 限定符和类型 方法和说明 CoreSubscriber<? super T>actual()已过时。Flux<T>asFlux()已过时。Return aFluxview of this sink.voidcancel()已过时。voidclear()已过时。static <E> UnicastProcessor<E>create()已过时。useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer()(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.static <E> UnicastProcessor<E>create(java.util.Queue<E> queue)已过时。useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.static <E> UnicastProcessor<E>create(java.util.Queue<E> queue, java.util.function.Consumer<? super E> onOverflow, Disposable endcallback)已过时。useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue, endCallback)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). TheonOverflowcallback is not supported anymore. To be removed in 3.5.static <E> UnicastProcessor<E>create(java.util.Queue<E> queue, Disposable endcallback)已过时。useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue, endCallback)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.ContextcurrentContext()已过时。Request aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.intcurrentSubscriberCount()已过时。Get how manySubscribersare currently subscribed to the sink.longdownstreamCount()已过时。Return the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.default voidemitComplete(Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)A simplified attempt at completing via theSinks.Many.tryEmitComplete()API, generating anonCompletesignal.default voidemitError(java.lang.Throwable error, Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)A simplified attempt at failing the sequence via theSinks.Many.tryEmitError(Throwable)API, generating anonErrorsignal.voidemitNext(T value, Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)已过时。A simplified attempt at emitting a non-null element via theSinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object)API, generating anonNextsignal.intgetBufferSize()已过时。Return the processor buffer capacity if any orInteger.MAX_VALUEjava.lang.ThrowablegetError()已过时。Current error if any, default to nullintgetPrefetch()已过时。The prefetch configuration of theFluxbooleanhasDownstreams()已过时。Return true if anySubscriberis actively subscribedjava.util.stream.Stream<Scannable>inners()已过时。Return aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)booleanisDisposed()已过时。Optionally return true when the resource or task is disposed.booleanisEmpty()已过时。booleanisTerminated()已过时。Has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?voidonComplete()已过时。voidonError(java.lang.Throwable throwable)已过时。voidonNext(T t)已过时。voidonSubscribe(org.reactivestreams.Subscription s)已过时。Implementors should initialize any state used bySubscriber.onNext(Object)before callingSubscription.request(long).Tpoll()已过时。voidrequest(long n)已过时。intrequestFusion(int requestedMode)已过时。Request a specific fusion mode from this QueueSubscription.java.lang.ObjectscanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)已过时。This method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place.intsize()已过时。voidsubscribe(CoreSubscriber<? super T> actual)已过时。An internalPublisher.subscribe(Subscriber)that will bypassHooks.onLastOperator(Function)pointcut.Sinks.EmitResulttryEmitComplete()已过时。Try to terminate the sequence successfully, generating anonCompletesignal.Sinks.EmitResulttryEmitError(java.lang.Throwable t)已过时。Try to fail the sequence, generating anonErrorsignal.Sinks.EmitResulttryEmitNext(T t)已过时。Try emitting a non-null element, generating anonNextsignal.-
从类继承的方法 reactor.core.publisher.FluxProcessor
dispose, hasCompleted, hasError, isSerialized, serialize, sink, sink, switchOnNext, wrap
-
从类继承的方法 reactor.core.publisher.Flux
all, any, as, blockFirst, blockFirst, blockLast, blockLast, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, buffer, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferTimeout, bufferUntil, bufferUntil, bufferUntilChanged, bufferUntilChanged, bufferUntilChanged, bufferWhen, bufferWhen, bufferWhile, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cache, cancelOn, cast, checkpoint, checkpoint, checkpoint, collect, collect, collectList, collectMap, collectMap, collectMap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectMultimap, collectSortedList, collectSortedList, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, combineLatest, concat, concat, concat, concat, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatDelayError, concatMap, concatMap, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapDelayError, concatMapIterable, concatMapIterable, concatWith, concatWithValues, contextCapture, contextWrite, contextWrite, count, create, create, defaultIfEmpty, defer, deferContextual, delayElements, delayElements, delaySequence, delaySequence, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delaySubscription, delayUntil, dematerialize, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinct, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, distinctUntilChanged, doAfterTerminate, doFinally, doFirst, doOnCancel, doOnComplete, doOnDiscard, doOnEach, doOnError, doOnError, doOnError, doOnNext, doOnRequest, doOnSubscribe, doOnTerminate, elapsed, elapsed, elementAt, elementAt, empty, error, error, error, expand, expand, expandDeep, expandDeep, filter, filterWhen, filterWhen, first, first, firstWithSignal, firstWithSignal, firstWithValue, firstWithValue, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMap, flatMapDelayError, flatMapIterable, flatMapIterable, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequential, flatMapSequentialDelayError, from, fromArray, fromIterable, fromStream, fromStream, generate, generate, generate, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupBy, groupJoin, handle, hasElement, hasElements, hide, ignoreElements, index, index, interval, interval, interval, interval, join, just, just, last, last, limitRate, limitRate, limitRequest, log, log, log, log, log, log, map, mapNotNull, materialize, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, merge, mergeComparing, mergeComparing, mergeComparing, mergeComparingDelayError, mergeComparingWith, mergeDelayError, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrdered, mergeOrderedWith, mergePriority, mergePriority, mergePriority, mergePriorityDelayError, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequential, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeSequentialDelayError, mergeWith, metrics, name, never, next, ofType, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureBuffer, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureDrop, onBackpressureError, onBackpressureLatest, onErrorComplete, onErrorComplete, onErrorComplete, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorContinue, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorMap, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorResume, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorReturn, onErrorStop, onTerminateDetach, or, parallel, parallel, parallel, publish, publish, publish, publish, publishNext, publishOn, publishOn, publishOn, push, push, range, reduce, reduce, reduceWith, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeat, repeatWhen, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, replay, retry, retry, retryWhen, sample, sample, sampleFirst, sampleFirst, sampleTimeout, sampleTimeout, scan, scan, scanWith, share, shareNext, single, single, singleOrEmpty, skip, skip, skip, skipLast, skipUntil, skipUntilOther, skipWhile, sort, sort, startWith, startWith, startWith, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribe, subscribeOn, subscribeOn, subscribeWith, switchIfEmpty, switchMap, switchMap, switchOnFirst, switchOnFirst, switchOnNext, switchOnNext, tag, take, take, take, take, takeLast, takeUntil, takeUntilOther, takeWhile, tap, tap, tap, then, then, thenEmpty, thenMany, timed, timed, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timeout, timestamp, timestamp, toIterable, toIterable, toIterable, toStream, toStream, toString, transform, transformDeferred, transformDeferredContextual, using, using, usingWhen, usingWhen, window, window, window, window, window, window, window, windowTimeout, windowTimeout, windowTimeout, windowTimeout, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowUntil, windowUntilChanged, windowUntilChanged, windowUntilChanged, windowWhen, windowWhile, windowWhile, withLatestFrom, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zip, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWith, zipWithIterable, zipWithIterable
-
从接口继承的方法 reactor.core.Fuseable.QueueSubscription
add, addAll, contains, containsAll, element, iterator, offer, peek, remove, remove, removeAll, retainAll, toArray, toArray
-
从接口继承的方法 reactor.core.Fuseable
fusionModeName, fusionModeName
-
从接口继承的方法 reactor.core.Scannable
actuals, from, isScanAvailable, name, parents, scan, scanOrDefault, stepName, steps, tags, tagsDeduplicated
-
-
-
-
构造器详细资料
-
UnicastProcessor
public UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue)
已过时。
-
UnicastProcessor
public UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue, Disposable onTerminate)
已过时。
-
UnicastProcessor
@Deprecated public UnicastProcessor(java.util.Queue<T> queue, java.util.function.Consumer<? super T> onOverflow, Disposable onTerminate)
已过时。
-
-
方法详细资料
-
create
@Deprecated public static <E> UnicastProcessor<E> create()
已过时。 useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer()(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.Create a newUnicastProcessorthat will buffer on an internal queue in an unbounded fashion.- 类型参数:
E- the relayed type- 返回:
- a unicast
FluxProcessor
-
create
@Deprecated public static <E> UnicastProcessor<E> create(java.util.Queue<E> queue)
已过时。 useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.Create a newUnicastProcessorthat will buffer on a provided queue in an unbounded fashion.- 类型参数:
E- the relayed type- 参数:
queue- the buffering queue- 返回:
- a unicast
FluxProcessor
-
create
@Deprecated public static <E> UnicastProcessor<E> create(java.util.Queue<E> queue, Disposable endcallback)
已过时。 useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue, endCallback)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). To be removed in 3.5.Create a newUnicastProcessorthat will buffer on a provided queue in an unbounded fashion.- 类型参数:
E- the relayed type- 参数:
queue- the buffering queueendcallback- called on any terminal signal- 返回:
- a unicast
FluxProcessor
-
create
@Deprecated public static <E> UnicastProcessor<E> create(java.util.Queue<E> queue, java.util.function.Consumer<? super E> onOverflow, Disposable endcallback)
已过时。 useSinks.many().unicast().onBackpressureBuffer(queue, endCallback)(or the unsafe variant if you're sure about external synchronization). TheonOverflowcallback is not supported anymore. To be removed in 3.5.Create a newUnicastProcessorthat will buffer on a provided queue in an unbounded fashion.- 类型参数:
E- the relayed type- 参数:
queue- the buffering queueendcallback- called on any terminal signalonOverflow- called when queue.offer return false and unicastProcessor is about to emit onError.- 返回:
- a unicast
FluxProcessor
-
getBufferSize
public int getBufferSize()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxProcessorReturn the processor buffer capacity if any orInteger.MAX_VALUE- 覆盖:
getBufferSize在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- processor buffer capacity if any or
Integer.MAX_VALUE
-
inners
public java.util.stream.Stream<Scannable> inners()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:ScannableReturn aStreamof referenced inners (flatmap, multicast etc)
-
scanUnsafe
public java.lang.Object scanUnsafe(Scannable.Attr key)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:ScannableThis method is used internally by components to define their key-value mappings in a single place. Although it is ignoring the generic type of theScannable.Attrkey, implementors should take care to return values of the correct type, and return null if no specific value is available.For public consumption of attributes, prefer using
Scannable.scan(Attr), which will return a typed value and fall back to the key's default if the component didn't define any mapping.- 指定者:
scanUnsafe在接口中Scannable- 覆盖:
scanUnsafe在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 参数:
key- aScannable.Attrto resolve for the component.- 返回:
- the value associated to the key for that specific component, or null if none.
-
onComplete
public void onComplete()
已过时。- 指定者:
onComplete在接口中org.reactivestreams.Subscriber<T>
-
tryEmitComplete
public Sinks.EmitResult tryEmitComplete()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyTry to terminate the sequence successfully, generating anonCompletesignal. The result of the attempt is represented as anSinks.EmitResult, which possibly indicates error cases.See the list of failure
Sinks.EmitResultin#emitComplete(EmitFailureHandler)javadoc for an example of how each of these can be dealt with, to decide if the emit API would be a good enough fit instead.- 返回:
- an
Sinks.EmitResult, which should be checked to distinguish different possible failures - 另请参阅:
Subscriber.onComplete()
-
onError
public void onError(java.lang.Throwable throwable)
已过时。- 指定者:
onError在接口中org.reactivestreams.Subscriber<T>
-
tryEmitError
public Sinks.EmitResult tryEmitError(java.lang.Throwable t)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyTry to fail the sequence, generating anonErrorsignal. The result of the attempt is represented as anSinks.EmitResult, which possibly indicates error cases.See the list of failure
Sinks.EmitResultin#emitError(Throwable, EmitFailureHandler)javadoc for an example of how each of these can be dealt with, to decide if the emit API would be a good enough fit instead.- 参数:
t- the exception to signal, not null- 返回:
- an
Sinks.EmitResult, which should be checked to distinguish different possible failures - 另请参阅:
Subscriber.onError(Throwable)
-
emitNext
public void emitNext(T value, Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyA simplified attempt at emitting a non-null element via theSinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object)API, generating anonNextsignal. If the result of the attempt is not asuccess, implementations SHOULD retry theSinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object)call IF the providedSinks.EmitFailureHandlerreturnstrue. Otherwise, failures are dealt with in a predefined way that might depend on the actual sink implementation (see below for the vanilla reactor-core behavior).Generally,
Sinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object)is preferable since it allows a custom handling of error cases, although this implies checking the returnedSinks.EmitResultand correctly acting on it. This API is intended as a good default for convenience.When the
Sinks.EmitResultis not a success, vanilla reactor-core operators have the following behavior:-
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_ZERO_SUBSCRIBER: no particular handling. should ideally discard the value but at that point there's noSubscriberfrom which to get a contextual discard handler. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_OVERFLOW: discard the value (Operators.onDiscard(Object, Context)) then callSinks.Many.emitError(Throwable, Sinks.EmitFailureHandler)with aExceptions.failWithOverflow(String)exception. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_CANCELLED: discard the value (Operators.onDiscard(Object, Context)). -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_TERMINATED: drop the value (Operators.onNextDropped(Object, Context)). -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZED: throw anSinks.EmissionExceptionmentioning RS spec rule 1.3. Note thatSinks.unsafe()never trigger this result. It would be possible for anSinks.EmitFailureHandlerto busy-loop and optimistically wait for the contention to disappear to avoid this case for safe sinks...
Might throw an unchecked exception as a last resort (eg. in case of a fatal error downstream which cannot be propagated to any asynchronous handler, a bubbling exception, a
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZEDas described above, ...).- 参数:
value- the value to emit, not nullfailureHandler- the failure handler that allows retrying failedSinks.EmitResult.- 另请参阅:
Sinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object),Subscriber.onNext(Object)
-
-
tryEmitNext
public Sinks.EmitResult tryEmitNext(T t)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyTry emitting a non-null element, generating anonNextsignal. The result of the attempt is represented as anSinks.EmitResult, which possibly indicates error cases.See the list of failure
Sinks.EmitResultin#emitNext(Object, EmitFailureHandler)javadoc for an example of how each of these can be dealt with, to decide if the emit API would be a good enough fit instead.Might throw an unchecked exception as a last resort (eg. in case of a fatal error downstream which cannot be propagated to any asynchronous handler, a bubbling exception, ...).
- 参数:
t- the value to emit, not null- 返回:
- an
Sinks.EmitResult, which should be checked to distinguish different possible failures - 另请参阅:
Subscriber.onNext(Object)
-
currentSubscriberCount
public int currentSubscriberCount()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyGet how manySubscribersare currently subscribed to the sink.This is a best effort peek at the sink state, and a subsequent attempt at emitting to the sink might still return
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_ZERO_SUBSCRIBERwhere relevant. (generally inSinks.Many.tryEmitNext(Object)). Request (and lack thereof) isn't taken into account, all registered subscribers are counted.- 返回:
- the number of subscribers at the time of invocation
-
asFlux
public Flux<T> asFlux()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyReturn aFluxview of this sink. Every call returns the same instance.- 返回:
- the
Fluxview associated to thisSinks.Many
-
onSubscribe
public void onSubscribe(org.reactivestreams.Subscription s)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:CoreSubscriberImplementors should initialize any state used bySubscriber.onNext(Object)before callingSubscription.request(long). Should furtheronNextrelated state modification occur, thread-safety will be required.Note that an invalid request
<= 0will not produce an onError and will simply be ignored or reported through a debug-enabledLogger.- 指定者:
onSubscribe在接口中org.reactivestreams.Subscriber<T>- 指定者:
onSubscribe在接口中CoreSubscriber<T>
-
getPrefetch
public int getPrefetch()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxThe prefetch configuration of theFlux- 覆盖:
getPrefetch在类中Flux<T>- 返回:
- the prefetch configuration of the
Flux, -1 if unspecified
-
currentContext
public Context currentContext()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:CoreSubscriberRequest aContextfrom dependent components which can include downstream operators during subscribing or a terminalSubscriber.- 指定者:
currentContext在接口中CoreSubscriber<T>- 覆盖:
currentContext在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- a resolved context or
Context.empty()
-
subscribe
public void subscribe(CoreSubscriber<? super T> actual)
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxAn internalPublisher.subscribe(Subscriber)that will bypassHooks.onLastOperator(Function)pointcut.In addition to behave as expected by
Publisher.subscribe(Subscriber)in a controlled manner, it supports direct subscribe-timeContextpassing.- 指定者:
subscribe在接口中CorePublisher<T>- 指定者:
subscribe在类中Flux<T>- 参数:
actual- theSubscriberinterested into the published sequence- 另请参阅:
Flux.subscribe(Subscriber)
-
request
public void request(long n)
已过时。- 指定者:
request在接口中org.reactivestreams.Subscription
-
cancel
public void cancel()
已过时。- 指定者:
cancel在接口中org.reactivestreams.Subscription
-
size
public int size()
已过时。- 指定者:
size在接口中java.util.Collection<T>
-
isEmpty
public boolean isEmpty()
已过时。- 指定者:
isEmpty在接口中java.util.Collection<T>
-
clear
public void clear()
已过时。- 指定者:
clear在接口中java.util.Collection<T>
-
requestFusion
public int requestFusion(int requestedMode)
已过时。从接口复制的说明:Fuseable.QueueSubscriptionRequest a specific fusion mode from this QueueSubscription.One should request either SYNC, ASYNC or ANY modes (never NONE) and the implementor should return NONE, SYNC or ASYNC (never ANY).
For example, if a source supports only ASYNC fusion but the intermediate operator supports only SYNC fuseable sources, the operator may request SYNC fusion and the source can reject it via NONE, thus the operator can return NONE as well to downstream and the fusion doesn't happen.
- 指定者:
requestFusion在接口中Fuseable.QueueSubscription<T>- 参数:
requestedMode- the mode requested by the intermediate operator- 返回:
- the actual fusion mode activated
-
isDisposed
public boolean isDisposed()
已过时。从接口复制的说明:DisposableOptionally return true when the resource or task is disposed.Implementations are not required to track disposition and as such may never return true even when disposed. However, they MUST only return true when there's a guarantee the resource or task is disposed.
- 指定者:
isDisposed在接口中Disposable- 返回:
- true when there's a guarantee the resource or task is disposed.
-
isTerminated
public boolean isTerminated()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxProcessorHas this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?- 覆盖:
isTerminated在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- has this upstream finished or "completed" / "failed" ?
-
getError
@Nullable public java.lang.Throwable getError()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxProcessorCurrent error if any, default to null- 覆盖:
getError在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- Current error if any, default to null
-
actual
public CoreSubscriber<? super T> actual()
已过时。
-
downstreamCount
public long downstreamCount()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxProcessorReturn the number of activeSubscriberor -1 if untracked.- 覆盖:
downstreamCount在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- the number of active
Subscriberor -1 if untracked
-
hasDownstreams
public boolean hasDownstreams()
已过时。从类复制的说明:FluxProcessorReturn true if anySubscriberis actively subscribed- 覆盖:
hasDownstreams在类中FluxProcessor<T,T>- 返回:
- true if any
Subscriberis actively subscribed
-
emitComplete
public void emitComplete(Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)
从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyA simplified attempt at completing via theSinks.Many.tryEmitComplete()API, generating anonCompletesignal. If the result of the attempt is not asuccess, implementations SHOULD retry theSinks.Many.tryEmitComplete()call IF the providedSinks.EmitFailureHandlerreturnstrue. Otherwise, failures are dealt with in a predefined way that might depend on the actual sink implementation (see below for the vanilla reactor-core behavior).Generally,
Sinks.Many.tryEmitComplete()is preferable since it allows a custom handling of error cases, although this implies checking the returnedSinks.EmitResultand correctly acting on it. This API is intended as a good default for convenience.When the
Sinks.EmitResultis not a success, vanilla reactor-core operators have the following behavior:-
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_OVERFLOW: irrelevant as onComplete is not driven by backpressure. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_ZERO_SUBSCRIBER: the completion can be ignored since nobody is listening. Note that most vanilla reactor sinks never trigger this result for onComplete, replaying the terminal signal to later subscribers instead (to the exception ofSinks.UnicastSpec.onBackpressureError()). -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_CANCELLED: the completion can be ignored since nobody is interested. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_TERMINATED: the extra completion is basically ignored since there was a previous termination signal, but there is nothing interesting to log. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZED: throw anSinks.EmissionExceptionmentioning RS spec rule 1.3. Note thatSinks.unsafe()never trigger this result. It would be possible for anSinks.EmitFailureHandlerto busy-loop and optimistically wait for the contention to disappear to avoid this case in safe sinks...
Might throw an unchecked exception as a last resort (eg. in case of a fatal error downstream which cannot be propagated to any asynchronous handler, a bubbling exception, a
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZEDas described above, ...).- 指定者:
emitComplete在接口中Sinks.Many<T>- 参数:
failureHandler- the failure handler that allows retrying failedSinks.EmitResult.- 另请参阅:
Sinks.Many.tryEmitComplete(),Subscriber.onComplete()
-
-
emitError
public void emitError(java.lang.Throwable error, Sinks.EmitFailureHandler failureHandler)从接口复制的说明:Sinks.ManyA simplified attempt at failing the sequence via theSinks.Many.tryEmitError(Throwable)API, generating anonErrorsignal. If the result of the attempt is not asuccess, implementations SHOULD retry theSinks.Many.tryEmitError(Throwable)call IF the providedSinks.EmitFailureHandlerreturnstrue. Otherwise, failures are dealt with in a predefined way that might depend on the actual sink implementation (see below for the vanilla reactor-core behavior).Generally,
Sinks.Many.tryEmitError(Throwable)is preferable since it allows a custom handling of error cases, although this implies checking the returnedSinks.EmitResultand correctly acting on it. This API is intended as a good default for convenience.When the
Sinks.EmitResultis not a success, vanilla reactor-core operators have the following behavior:-
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_OVERFLOW: irrelevant as onError is not driven by backpressure. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_ZERO_SUBSCRIBER: the error is ignored since nobody is listening. Note that most vanilla reactor sinks never trigger this result for onError, replaying the terminal signal to later subscribers instead (to the exception ofSinks.UnicastSpec.onBackpressureError()). -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_CANCELLED: the error can be ignored since nobody is interested. -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_TERMINATED: the error unexpectedly follows another terminal signal, so it is dropped viaOperators.onErrorDropped(Throwable, Context). -
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZED: throw anSinks.EmissionExceptionmentioning RS spec rule 1.3. Note thatSinks.unsafe()never trigger this result. It would be possible for anSinks.EmitFailureHandlerto busy-loop and optimistically wait for the contention to disappear to avoid this case in safe sinks...
Might throw an unchecked exception as a last resort (eg. in case of a fatal error downstream which cannot be propagated to any asynchronous handler, a bubbling exception, a
Sinks.EmitResult.FAIL_NON_SERIALIZEDas described above, ...).- 指定者:
emitError在接口中Sinks.Many<T>- 参数:
error- the exception to signal, not nullfailureHandler- the failure handler that allows retrying failedSinks.EmitResult.- 另请参阅:
Sinks.Many.tryEmitError(Throwable),Subscriber.onError(Throwable)
-
-
-